The Best Soil for Growing Cannabis
The Best Soil for Growing Cannabis
When it comes to growing cannabis, choosing the right soil is crucial for healthy plant growth and high-quality yields. Soil provides the essential nutrients that marijuana plants need to thrive. In this article, we will cover the basics of soil and how it affects cannabis plants, as well as different types of soil and substrates that are optimal for growing cannabis.
The Role of Soil in Cannabis Plant Growth
Soil plays a vital role in the growth and development of cannabis plants. Soil provides a stable medium for plants to grow in and acts as a reservoir for water and nutrients. The nutrients in the soil are vital for plant growth, and they can be divided into three categories: primary, secondary, and micronutrients.
There are 18 essential nutrients that cannabis requires for optimal growth and yield. The availability of these nutrients in the soil can be dependent on the soil’s pH.
The pH level of the soil is also crucial for healthy plant growth. Cannabis plants prefer a slightly acidic soil pH of between 5.8 and 6.3. If the pH level is too high or too low, it can “lock out” nutrients to the plant, leading to stunted growth and poor yields.
Soil vs Potting Mix
Soil and potting mix are very different growing mediums. Soil is the natural layer of earth that covers the surface of the ground, consisting of a mixture of minerals, organic matter, water, air, and microorganisms. Soil can vary in texture, pH level, and nutrient content depending on its location and composition.
On the other hand, potting mix is a man-made growing medium that is specifically designed for container gardening.
Potting mixes are made from a blend of organic matter such as peat moss, composted bark, and coconut coir, as well as other ingredients such as perlite or rice hulls. These components are carefully mixed to create a lightweight, well-draining growing medium that provides the right balance of nutrients and moisture for container-grown plants.

One of the main differences between soil and potting mix is that soil is heavier and denser, while potting mix is lighter and fluffier. This is because potting mix is designed for container-grown plants, while soil is found outside and is full of minerals that are broken down from rocks.
Soil is made up of different size rock particles that describe its texture, this influences its water-holding abilities and drainage.
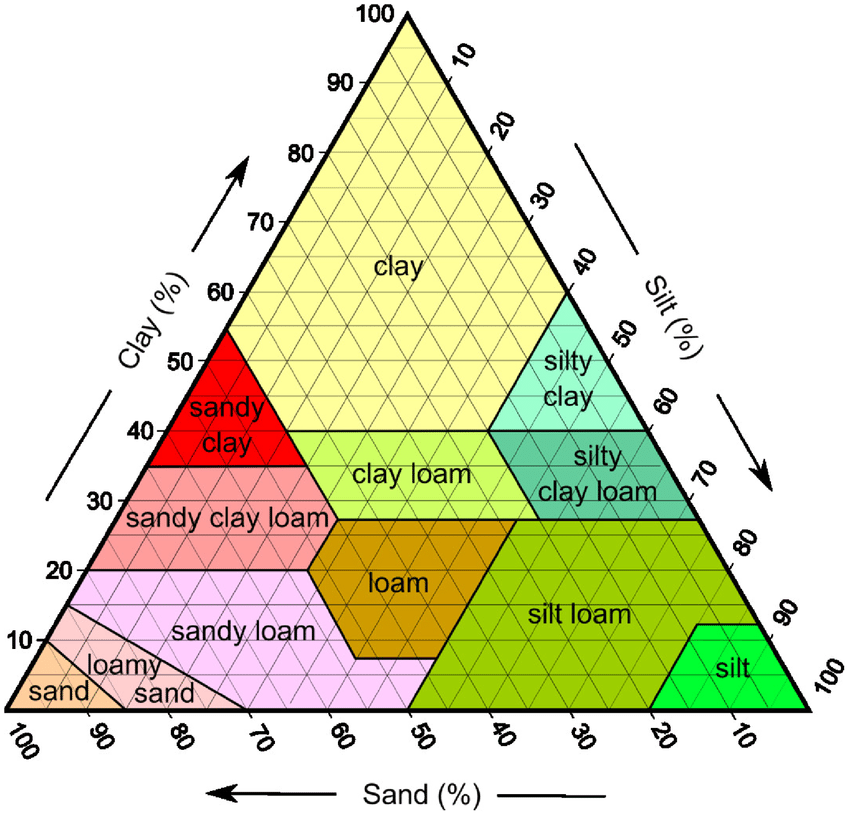
Soil Texture and Cannabis Plant Growth
Soil texture plays a crucial role in cannabis plant growth. The three basic types of soil texture are clay, sand, silt, and loam which contains equal portions of all three of the soil texture.
Each type of soil has its unique characteristics that affect plant growth.
- Sandy soil has large particles and is easy to work with. It drains quickly, which can be a disadvantage for highly mobile nutrients like Nitrogen that will wash away as the water drains.
- Silt soil has medium-sized particles and holds moisture well.
- Clay soil has small particles and is very dense, which makes it difficult for water to penetrate if it becomes compacted. It also has the highest cation exchange capacity (CEC) of all the soil textures.
- Loam soil is a mix of sand, silt, and clay and is considered the ideal soil type for growing cannabis. Loam soil provides good drainage, and water retention, and is easy to work with.
All soil textures have an organic fraction that is formed from living organisms, it consists primarily of Carbon and Nitrogen and acts as a nutrient reservoir for plants. It includes living organisms, decaying organisms, and decomposing animal residues.
Microorganisms use these residues as their food source and are constantly decomposing soil organic matter. The residue left behind from this decomposition is humus.
Humus is nature’s compost. It’s one of the best composts for weed because of its ability to form both ionic and covalent bonds, necessary for nutrient cycling. This means it breaks down minerals making them more available for plants.
The organic fraction of soil is the most important portion of soil for nutrient cycling. You can improve all soil types by increasing soil organic matter through a variety of cover crops, manures, and compost.
The organic fraction is what potting mix is primarily based on, but it doesn’t contain nearly as many minerals as soil.
Substrates for Potting Mixes
Growers often use a marijuana soil mix or cannabis potting mix that includes various substrates such as peat moss, coco coir, and compost like earthworm castings or vermicompost.
Peat moss is a popular substrate as it is highly absorbent and retains water well.
Coco coir is an eco-friendly alternative to peat moss and is made from coconut husks. It is highly porous and retains water well, making it an excellent substrate for cannabis plants.
Compost is a nutrient-rich organic matter that is produced from the decomposition of organic materials such as food scraps, yard waste, and other plant matter. The best composts for cannabis are often referred to as “black gold” because of their ability to improve soil fertility and support plant growth.
Earthworm castings are rich in nutrients and provide a slow-release fertilizer for cannabis plants and when they are composted they become vermicompost.

Living Soil and Slow-Release Nutrients
Living soil is a popular option for cannabis growers as it contains microorganisms and beneficial bacteria that help break down organic matter and release nutrients to the plants over time. This type of cannabis soil is highly sustainable and promotes healthy plant growth. It typically contains organic fertilizers that are broken down over time by microbes. Examples of these slow-release nutrients are bat guano, glacial rock dust, and worm castings.
Living soil tends to get better over time and is the most sustainable option for growing cannabis. It’s often considered the best organic soil for cannabis.
Living soil provides the most microbial diversity which can increase terpenes and improve the overall flavor and smell of your cannabis.
Microorganisms also aid in defending your plants against pests and pathogens, creating more robust and healthier plants.
You can learn more about growing in living soil by listening to the Sun Grown podcast.
What Soil for Marijuana?
The best soil for cannabis will have proper aeration and drainage, microbial diversity, balanced nutrient ratios, and a high CEC. This is the same when looking for the best soil for indoor weed plants and outdoor gardens.
The soil should allow oxygen to circulate around the roots while also retaining enough moisture for the plant to thrive. A variety of microorganisms and a balanced nutrient profile is essential. And soils with a high CEC will make nutrients more accessible to the plant.
Most bagged potting mixes marketed for cannabis contain these essential requirements, but you can make your own.
Building the best potting mix for marijuana can be a fun and affordable alternative to store-bought. It can be cheaper than buying bags and it allows you to add specific amendments.
This basic potting mix for cannabis recipe is based on volume:
- 1/3 Sphagnum Peat Moss and/or Coco Coir
- 1/3 Aeration (Rice Hulls*, Pumice, Vermiculite, Perlite)
- 1/3 Compost
- 5-10% total volume Biochar**
- Amendments (Neem Meal, Glacial Rock Dust, Soft Rock Phosphate, Crustacean Meal, Kelp Meal, etc.)
* Rice hulls are the most sustainable option for aeration.
** Biochar increases your CEC and provides homes for microbes for cannabis potting/soil.

Conclusion
Choosing the optimal soil for growing marijuana is essential for plant health and exceptional yields. Whether using store-bought potting soil or creating a living soil mix, or growing in the ground, cannabis growers should pay close attention to the soil’s texture, drainage, and nutrient content. With the right soil and proper care, marijuana plants can thrive and produce high-quality buds.









